Breakthrough science enabled by LUMI
Researchers across Europe in academia and industry have harnessed LUMI supercomputer’s computing power to accelerate discoveries, tackle society’s most pressing challenges, and drive innovation across diverse scientific disciplines. Since its launch, LUMI has provided cutting-edge high-performance computing (HPC) and AI capacity for around 3500 research projects in academia and industry. There have been over 280 articles published in peer-reviewed scientific journals between autumn 2022 and autumn 2025* that acknowledge access to LUMI.
Highlights include 34 articles in the prestigious Nature and its family of journals, as well as publications in other leading titles such as Science and Cell. In addition, LUMI was cited in hundreds of conference papers and preprints.
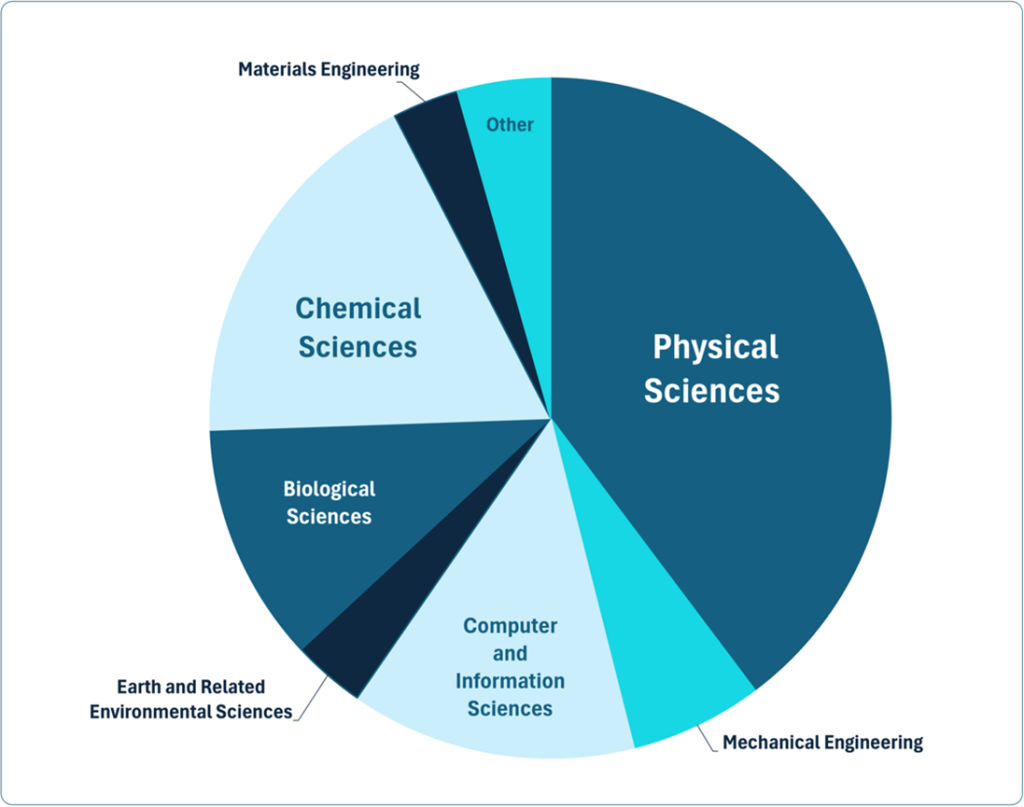
The articles represent a wide range of disciplines with 30 scientific disciplines presented in the OECD taxonomy used in the LUMI project allocation data. The majority of the projects fall under natural sciences like physics, chemistry and biology. However, there are also several articles related to engineering, and for example, some covering topics relevant to agriculture, health and medicine. Additionally, many of them are interdisciplinary in nature.
Selected highlights
Below are selected highlights from scientific publications that demonstrate LUMI’s significant impact in advancing discoveries in topics such as:
Health and life sciences
- Miguel Graça et al: Distributed transformer for high order epistasis detection in large-scale datasets
in Nature Scientific Report. - Petra Čechová et al: Mechanistic insights into interactions between ionizable lipid nanodroplets and biomembranes
in Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Friederike Barkmann et al: Machine learning training data: over 500,000 images of butterflies and moths (Lepidoptera) with species labels
in Nature Scientific Data. - Antti Pihlajamäki et al: GraphBNC: Machine Learning-Aided Prediction of Interactions Between Metal Nanoclusters and Blood Proteins
in Advanced Materials.
Climate science
- Nils Wedi et al: Implementing digital twin technology of the earth system in Destination Earth
in Journal of the European Meteorological Society. - Destination Earth’s Climate Change Adaptation Digital Twin was shortlisted for the ACM Gordon Bell Prize for Climate Modelling 2025.
Physics and engineering
- Jörn Warnecke et al: Numerical evidence for a small-scale dynamo approaching solar magnetic Prandtl numbers
in Nature Astronomy. - Daniele Massaro et al: Direct numerical simulation of the turbulent flow around a Flettner rotor
in Nature Scientific Reports. - The code used in the latter publication, Neko, was also shortlisted for the 2023 ACM Gordon Bell Prize.
Professor Maarit Korpi-Lagg from the Department of Computer Science at Aalto University, Finland, who was one of the authors of the Nature Astronomy publication stated that:
“Faster calculations also mean considerable energy savings. For years I have felt bad thinking about how much environmental resources supercomputers require, but now working on one of the most environmentally friendly supercomputers in the world means this is a great weight off my mind.”
Quantum mechanics
- Daniel Pęcak et al: Time-dependent nuclear energy-density functional theory toolkit for neutron star crust: dynamics of a nucleus in a neutron superfluid
in Physical Review X.
Dr. Daniel Pęcak from the Institute of Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences, the main contributor to the article and principal investigator of the LUMI project, said:
“Our group consistently seeks access to the latest high-performance computing (HPC) machines. These resources are essential for exploring Fermi systems with the necessary high resolution and large volumes, which are crucial for studying the microscopic properties of neutron stars. The requirement to model not only the nucleus but also the superfluid adds significant complexity, making it challenging to consider finite-size effects accurately. With supercomputing resources, studying effective mass using our approach is possible. Therefore, LUMI’s contribution to our research is invaluable.”
Impact across society
HPC has become a cornerstone of modern scientific discovery and technological progress. Across disciplines researchers rely on supercomputers to process vast datasets, run complex simulations, and generate insights that would be impossible with conventional computing resources. In Europe, strategic investments in HPC infrastructure are not only driving breakthroughs in fundamental research but also enabling practical solutions to some of the most pressing global challenges.
LUMI empowers scientists to tackle problems at previously unimaginable scales, accelerating innovation and fostering collaboration across borders. Its impact extends beyond academia, influencing industry, policy, and society at large.
“These scientific publications in leading journals showcase the importance of supercomputer research infrastructures such as LUMI for science and society. They demonstrate that Europe’s sustained investments in supercomputing infrastructure are delivering tangible results – advancing research, fostering innovation, and addressing global challenges,” says Pekka Manninen, director of LUMI.
*Data about the articles published between autumn 2022 and autumn 2025 was gathered through Google Scholar. Analysis of the articles was conducted with the support of GTP-5-enabled Microsoft Copilot, and the results were reviewed to ensure their accuracy.
Photo: Mikael Kanerva, CSC.
Read more
- To apply for access to LUMI’s computing resources, please have a look at the Get started sectionon the LUMI website
- LUMI supercomputer
- High-performance computing for companies
